The ms-settings:windowsupdate-history setting allows users to review Windows 10 und 11 Update history.
This page provides details about previous updates, including successful and failed installations. The update history provides information about which feature updates, quality updates, drivers, and other system components have been installed and allows you to uninstall certain updates if necessary. This feature is especially important for keeping track of system stability and for identifying the cause of problems with updates more quickly.
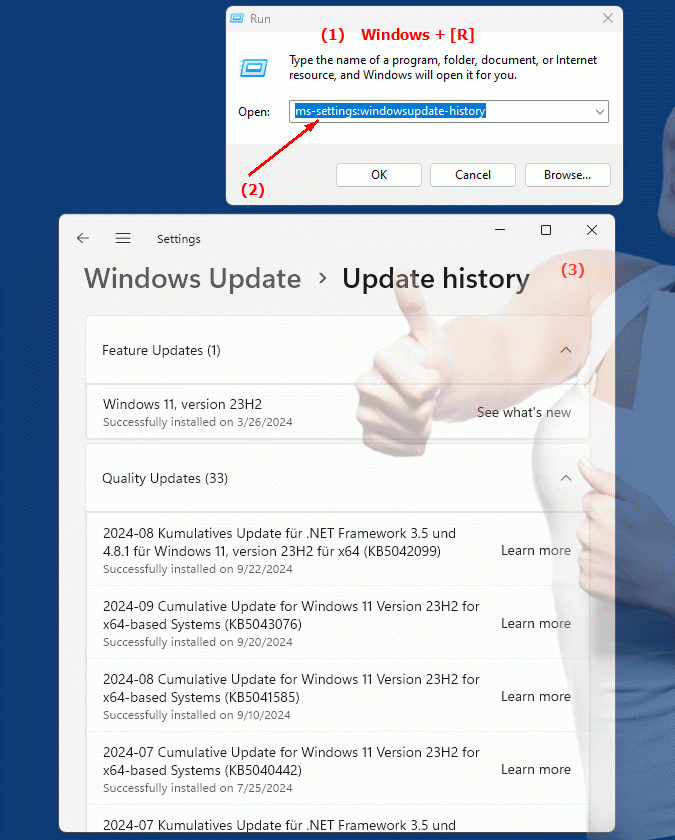
1. ms-settings:windowsupdate-history
2. Availability under Windows
3. Other useful commands in the Windows settings
1. The Command ms-settings:windowsupdate-history
1. Combine the Windows R keys for quick access.2. Use the command: ms-settings:windowsupdate-history to perform the desired step.
(The command is also useful for creating a desktop shortcut.)
3. Select OK or press [Enter] to confirm.
(... see Image-1 Point 1 to 3)
You can now access the settings explained above in your Windows 10, 11 or 12 operating system.
This is how the problems and questions listed below are addressed.
1b. This is how the problems and questions listed below are addressed.
How to check Windows Update history?What details can be viewed in the Windows Update history?
What does the update history show about the installed updates?
If you have problems with updates, can you use the history to find the cause?
How can I view system components and drivers in Windows Update history?
Is it possible to remove certain updates from the list of installed updates?
How can I view Windows Update history on another computer if my own is unavailable?
Is there a way to customize or configure the behavior of automatic updates?
How often should you check the Windows Update history to ensure that the system is running stable?
2. It is available starting with the corresponding build numbers in Windows 10, 11 and 12!
Here is a detailed description of the availability of the “ms-settings:windowsupdate-history” feature in the different Windows versions, including build numbers and specific improvements:
Windows 10
- Availability:
From Windows 10 version 1703 (Creators Update, March 2017)
- Build number:
15063
The “ms-settings:windowsupdate-history” feature was introduced in Windows 10 to provide users with easier access to their update history. This setting allows users to view and manage the complete history of Windows Updates, including information about:
1. Feature updates:
Major version changes to Windows (such as updating to a new version of Windows 10).
2. Quality Updates:
Security and performance improvements delivered on a regular basis.
3. Driver updates:
Automatically installed drivers for hardware components.
4. Optional Updates:
Manually installable updates that include additional features or drivers.
5. Failed Updates:
Updates that did not install successfully are listed with error codes.
Users can also directly uninstall updates that are causing problems. A link to the "Installed Updates" leads to the Control Panel options to get detailed information about major updates or packages.
Key features in Windows 10:
- Display feature, quality and driver updates.
- List of update errors and possibility to fix them.
- Direct access to uninstall problematic updates.
Windows 11
- Availability:
From Windows 11 version 21H2 (November 2021 Update)
- Build number:
22000
In Windows 11, Update history has been integrated into the redesigned "Windows Update" interface. The "ms-settings:windowsupdate-history" feature still provides access to all previous updates, but in a more modern and user-friendly design. The new user interface in Windows 11 is more clearly structured and offers easier navigation through the various update categories, including:
1. Feature updates:
Updates to new versions of Windows.
2. Quality Updates:
Monthly and cumulative updates.
3. Driver updates and other important updates.
Windows 11 places particular emphasis on optimizing update mechanisms so that updates can be installed more efficiently in the background without disrupting the user's work. Users still have the option to uninstall problematic updates if they cause system instability or other problems.
Improvements in Windows 11:
- Improved user interface with clear information about each installed update.
- Integration of AI-driven recommendations for the best time to install updates.
- Better optimization of update processes to use fewer system resources and update the system in the background.
Windows 12
- Availability:
Windows 12 is also expected to support the ms-settings:windowsupdate-history setting, with exact details and build number to be announced with the final release.
Windows 12 is expected to further improve update history management. The interface may be further simplified and additional options may be added to optimize the frequency of update notifications and flexibility in installing updates. In addition, deeper insight into the specific changes that come with each update could be made available directly in the UI to give users more control and understanding of their system changes.
Expected improvements in Windows 12:
- Granular control over update notifications.
- Optimized update history display with more detailed descriptions.
- Improved options for selecting and uninstalling updates.
Summary
- Windows 10:
Available starting with version 1703 (Build 15063), provides basic access to update history, including feature, quality, and driver updates.
- Windows 11:
Available from version 21H2 (Build 22000), with a revised, more user-friendly interface and optimized update processes.
- Windows 12:
Expected to continue supporting the feature, with possible improvements in user controls and detailed update information.
The “ms-settings:windowsupdate-history” setting is a central feature in all newer Windows versions (from Windows 10 version 1703) for keeping track of past updates and performing troubleshooting. While Windows 10 provides a solid foundation for this functionality, Windows 11 brings a modernized interface and improved update management. Windows 12 is expected to provide further optimizations and new features for managing and controlling updates.
