Before you do a new installation of Windows 11 you can manage network passwords and back them up and restore them to Win 11!Saving credentials enables Windows 11, 10, ... to automatically log on to websites and other computers. The credentials are saved on your computer and are used for Windows itself and other programs, APPS, applications, web browsers, ... You can securely transfer the credentials saved into other Windows computers! 1.) ... Manage, backup and restore network passwords!
|
| (Image-1) Windows 11: Manage network passwords, restore backup! |
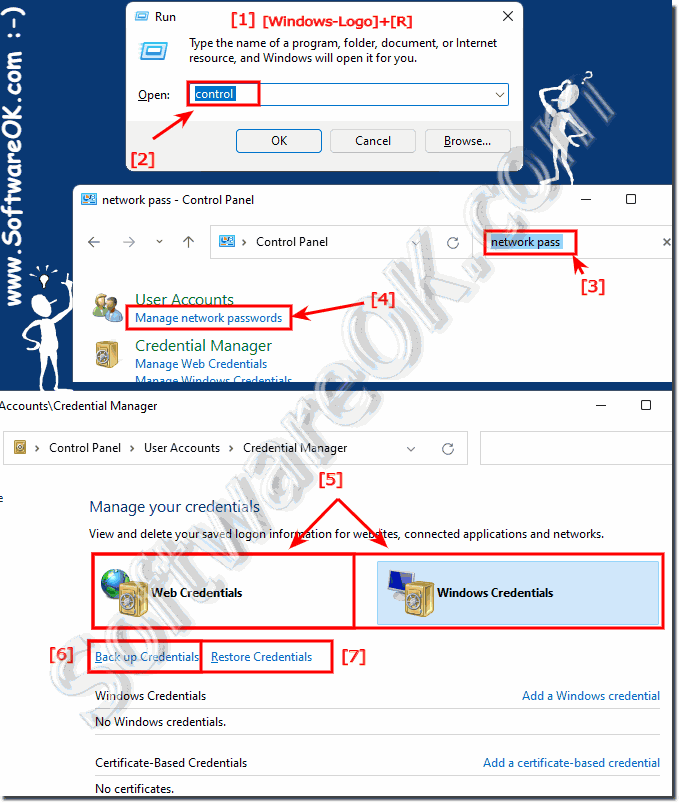 |
2.) What are network passwords, is that the Windows 11 login?
No, these are FTP, Remote Desktop and other network passwords, the Windows login is not saved here.
See also: ►► Automatically log in to Windows 11 / Autologin?
Network passwords are passwords used to authenticate and secure access to a network or devices on a network. They can take various forms and are used to restrict access to certain resources on a network. Network passwords can be used for various purposes, including:
Windows login:
Yes, the password you use to log in to your Windows operating system is an example of a network password. This password allows access to your computer and its associated resources.
Wi-Fi Password:
The password you use to connect to a wireless network is also a network password. It protects your WiFi from unauthorized access.
Router Password:
If you have a router on your home network, you usually need to log in to the router management interface with a password. This password is used to protect your router's settings.
Website and online accounts:
When you log into websites or online services, you typically use usernames and passwords to access your account. These passwords are used to secure your access to the respective online services and are also examples of network passwords.
So, broadly speaking, network passwords are passwords used in a network context to control access to various resources and ensure that only authorized users can access those resources. Windows logins and WiFi passwords are just two examples of such network passwords.
3.) What should I watch out for with network passwords?
Everyone knows the rules for passwords, the longer and more unpredictable the better, here it really depends on the length, the longer the more secure and even better if the password or parts of the password are not in "Spelling Dictionary" or anywhere else.As with Windows 10, ... and MS Server, so also with the new MS Windows 11 ... it makes sense that you save user names and passwords, access data and other passwords on removable media, USB stick and not on the internal hard drive of the Back up Windows PC. Useful if the Windows computer no longer works during the restoration or if the restoration is to be carried out on a different PC.
See also:
►► How can I find out the current WiFi password in Windows?
►► Log in automatically under Windows 11 / Autologin?
►► What is a password?
Use complex passwords that consist of a combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers and special characters. Avoid easy-to-guess passwords like “123456” or “password”. Use longer passwords as they are generally more secure. Use different passwords for different services and devices to minimize the risk of all of your credentials being compromised in the event of a data breach.
When dealing with network passwords, there are a few important aspects to keep in mind to ensure the security of your network:
Update:
Change your passwords regularly, especially for important accounts.
Update the default password of your router or other network devices.
Storage and management:
Avoid storing passwords in unencrypted files or on pieces of paper.
Use password managers to securely store and manage passwords.
Access permissions:
Restrict access to your network and devices to only authorized users.
Assign different access rights to ensure that users can only access the resources that are relevant to them.
Secure communications:
Use encrypted connections (e.g. WPA2 or WPA3 for wireless networks) and VPNs when transmitting sensitive data over your network.
Two-factor authentication (2FA):
Where possible, enable 2FA on important accounts to add an additional layer of security.
Monitoring and Updates:
Monitor your network for suspicious activity.
Keep your network devices' firmware and software up to date to address known security vulnerabilities.
Phishing protection:
Be wary of emails or messages asking for your network passwords. Phishing attacks are common and attempt to trick users into revealing their login credentials.
Education:
Train everyone on your network to use passwords wisely and securely so they are aware of the importance of network security. By following these best practices, you will help protect the security of your network and your personal information.
FAQ 85: Updated on: 26 October 2023 06:54
