The solution to format a formatted HDD or SSD to NTFS on Windows Desktop PCs or in example on Microsoft Web Server 2019!Content: 1.) ... Format a formatted HDD or SSD
|
| (Image-1) Format the SSD hard drive to NTFS under Windows 10! |
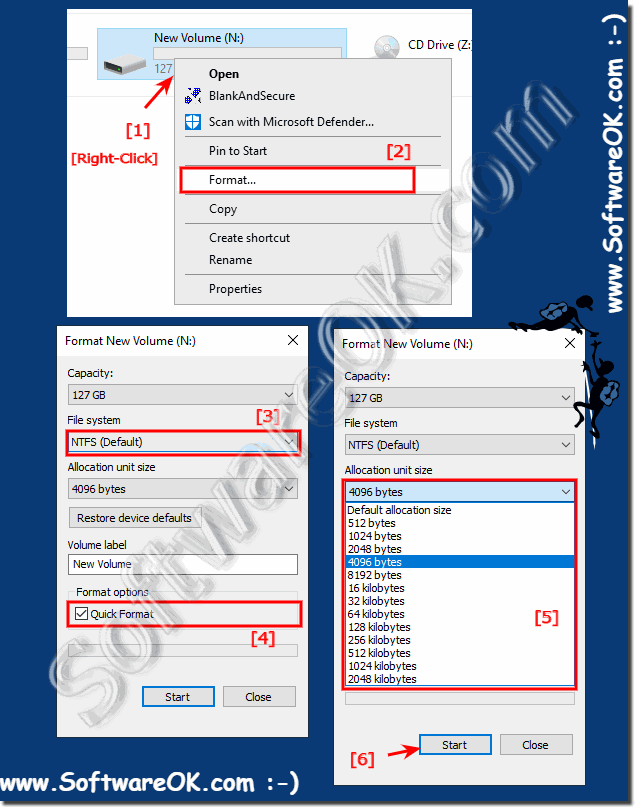 |
4.) Are there any advantages to reformatting a hard drive?
Yes, reformatting a hard drive offers several benefits:1. Improved performance:
Reformatting deletes old file system structures, which can optimize the hard drive and improve performance. This is particularly noticeable if the hard drive has been used for a long period of time and is fragmented.
2. Malware and virus removal:
Reformatting a hard drive deletes all existing files and programs, including any malware or viruses that may be present. This can help make the system more secure.
3. Clean up unnecessary files:
Over time, a hard drive can accumulate a lot of temporary and unnecessary files. Formatting deletes these files, resulting in system cleanup and freeing up disk space.
4. Troubleshoot file system problems:
Sometimes file system errors can occur, which can lead to instability or data loss. Reformatting recreates the file system, which can help resolve such issues.
5. Preparing for an Operating System Reinstallation:
If you intend to reinstall the operating system, reformatting the hard drive is often the first step. This will return the hard drive to a clean state required for a reinstall.
However, it is important to note that reformatting a hard drive will permanently delete all data on it. Therefore, important files should be backed up before formatting.
5.) What are the pitfalls and mistakes when formatting a hard drive!
When formatting a hard drive, there are some pitfalls and mistakes that should be avoided:1. Incorrect selection of formatting method:
Depending on which file system and partitioning method are needed, the correct options must be selected. For example, formatting in the wrong file system or with the wrong partitioning method can cause incompatibility issues.
2. Important data not backed up:
Before formatting a hard drive, you should make sure that all important data has been backed up. Formatting results in the irreversible deletion of all data stored on the hard drive.
3. Incorrect disk selection:
It is important to ensure that the correct disk is selected for formatting. Formatting the wrong hard drive can result in data loss on other drives.
4. Inadequate preparation:
Before you start formatting, make sure that no programs or processes are accessing the hard drive to be formatted. Active processes can hinder formatting or corrupt data.
5. Firmware and Driver Compatibility:
Make sure your hardware components' firmware and drivers are compatible with the file system and formatting method you plan to use. Incompatibilities can lead to malfunctions or data loss.
6. Aborting the formatting process:
Do not interrupt the formatting process prematurely as this may result in data corruption or an unusable file system.
7. Hard drive not checked after formatting:
After formatting, it is recommended to check the hard drive for errors to ensure that there are no defects and that the file system was created correctly.
By being aware of these potential sources of error and taking appropriate precautions, you can format a hard drive safely and effectively.
6.) Are there any differences if I format on Windows, MacOS or Linux?
Yes, there are differences when formatting a hard drive on different operating systems such as Windows, macOS and Linux. These differences mainly concern the file systems supported, the formatting tools available, and the way the formatting process is performed. Here are some of the key differences:
1. Supported file systems:
Each operating system has its own supported file systems. For example, Windows supports file systems such as NTFS, FAT32 and exFAT, macOS supports HFS+ and the newer APFS, while Linux supports a variety of file systems such as Ext4, Btrfs and XFS. When formatting a hard drive, you need to make sure that the file system you choose is compatible with the operating system you plan to use it on.
2. Formatting tools:
Each operating system has its own built-in formatting tools as well as third-party tools from manufacturers. For example, Windows offers the Disk Management or Format utility through File Explorer, macOS offers Disk Utility, and Linux offers commands like mkfs or GUI tools like GParted. These tools have different interfaces and features, but the basic formatting process remains similar.
3. Command-line options:
Linux operating systems often offer more flexibility and advanced command-line options for formatting hard drives compared to Windows and macOS. Advanced users can use certain commands on Linux operating systems to customize certain options or create different file systems.
4. Partitioning Methods:
The way partitions are created and managed on hard drives may vary depending on the operating system. For example, Windows often uses the MBR (Master Boot Record) or the newer GPT (GUID Partition Table) to partition hard drives, while macOS typically uses the GPT format. Linux is more flexible and supports both MBR and GPT as well as other partitioning schemes.
5. Integration into the operating system:
The integration of the formatting process into the operating system can vary. For example, some operating systems can automatically detect drives and offer formatting options, while others may require manual steps to access the formatting tool.
So overall, there are differences in formatting a hard drive on different operating systems, but the basic process remains similar:
you select the file system you want and perform the formatting process.
FAQ 7: Updated on: 23 May 2024 11:19
