If the CPU frequency is not always the same, it can have different causes, it does not have to be a faulty / defective CPU!Contents: 1.) ... The processor / CPU frequency can definitely vary!
|
| (Image-1) Simply repeat the CPU frequency Test! |
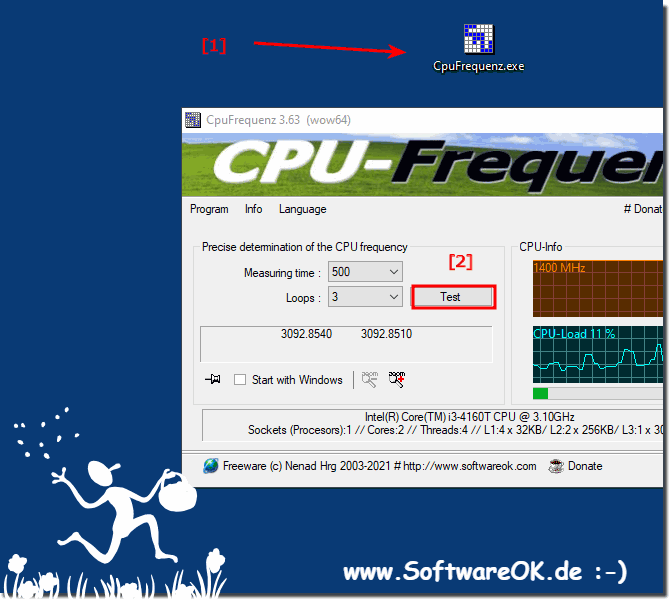 |
2.) Other reasons If the CPU frequency is not always the same!
CPU frequencies do not remain constant and can vary for a variety of reasons, including:
1. Dynamic Frequency Scaling (DFS) Most modern CPUs support dynamic frequency scaling, also known as CPU throttling or speed stepping. This technology allows the CPU to adjust its clock speed on the fly based on current workload and power management policies. When the CPU is idle or under light load, it can reduce its frequency to save power and reduce heat generation. Conversely, when the workload is high, the frequency can be increased to improve performance.
2. Power managementAs mentioned earlier, power management plays an important role in varying CPU frequency. Lowering the CPU frequency reduces power consumption, which is crucial for laptops and mobile devices to extend battery life. Desktops and servers also use power management to save energy and reduce cooling costs.
3. Temperature Management CPUs generate heat when operated at high frequencies. To avoid overheating, CPUs can dynamically reduce their frequency when the temperature exceeds a certain threshold. This is a security mechanism to protect the CPU from damage.
4. Turbo BoostMany modern CPUs have a feature called Turbo Boost or Turbo Core. This technology allows the CPU to temporarily increase its frequency above the base clock frequency when additional processing power is needed. When the workload requires it, Turbo Boost can provide a performance boost for short periods of time.
5. Hardware and Firmware Settings Some CPUs allow users or system administrators to manually adjust the CPU frequency through BIOS/UEFI settings or software utilities. For example, overclocking is intentionally setting the CPU to run at a higher frequency than the base clock frequency.
6. Operating system controlsThe operating system plays a role in managing CPU frequency through power management policies. It can adjust CPU frequency based on system power profile and user-defined settings. Different performance profiles, such as Options such as Symmetrical or High Performance can affect the behavior of the CPU frequency.
7. Workload Variation CPU frequency may vary depending on the type of workload. Intensive tasks like video rendering or gaming can cause the CPU to run at higher frequencies, while lighter tasks like web browsing can cause the CPU to run at lower frequencies.
8. Thermal limitationsFor laptops and smaller form factor devices, space and cooling limitations can limit CPU clocking under heavy load. The CPU may not be able to maintain its maximum rated frequency for extended periods of time without reaching critical temperatures, so it adjusts its frequency accordingly.
In summary, CPU frequencies vary due to a combination of dynamic frequency scaling, power management, temperature control, workload requirements, and user or system settings. This flexibility allows CPUs to balance performance, power consumption, and thermal considerations to meet the needs of different computing scenarios.
FAQ 5: Updated on: 6 May 2024 18:34
