The size of the currently available physical memory variable. Here are some information!Here are the short info, who wants to know more, can Googe, Bingo or Yahoo, or just contact me and question the relevant term and I write then extensive information. About the main memory you could write several bookbands is almost like all the other stuff! Please always use ... the latest version of QuickMemoryTestOK!
Content: 1.) ... Based on the Task Manager, known from XP, why not under 10 ;-)!
|
| (Picture 1) The task manager from Windows XP now also for Windows 10! |
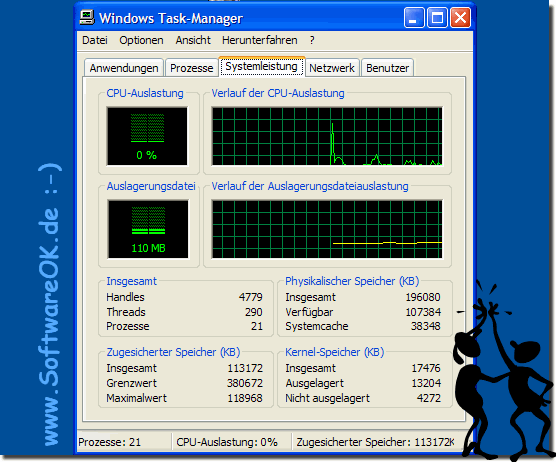 |
Excerpt from the Microsoft (c) help:
Paging File Usage History
A chart that shows the paging file's utilization over time. The sample displayed in the chart depends on the value selected in the View menu under Refresh Rate.
Total
totals for the number of handles, threads, and processes that are running on the computer.
Guaranteed Memory (KB) Memory allocated to
the programs and / or the operating system. Because of memory being copied to the paging file (called virtual memory), the value listed under Maximum can exceed the maximum physical memory. The Total value is the same as the value shown in the Paging File Usage History graph.
Physical Memory (KB)
The total physical memory (also called RAM) installed on the computer. Available indicates the amount of free space that can be used. System cache specifies the actual amount of physical memory used to allocate pages of open files.
Kernel Memory (KB)
Memory used by the kernel drivers and device drivers of the operating system. Outsourced refers to storage that can be copied to the paging file, which frees up physical memory. The physical memory can then be used by the operating system. Non-paged refers to memory that remains in physical memory and is not copied to the paging file.
2.) The memory terms!
Physical Memory
The size of the actual physical memory RAM, for example, is 32GB for 2 x 16GB.
Physical Available (Physical Available)
The size of the physical memory currently available. This is the amount of physical memory that can be reused immediately without having to first write the content to disk. This is the sum of the size of the standby, free, and null lists.
System Cache
The size of the system cache in pages. This is the size of the standby list plus the system work set.
Kernel Total
The amount of memory in the paged and nonpaged kernel pools.
Kernel Paged
The storage that is currently in the paged kernel pool.
Kernel Nonpaged
The memory currently in the non-paged kernel pool .
Block Size (Page Size)
The size of a memory block in bytes.
Handle Count Handle the
current number of open memory.
Process Count
The current number of processes.
Number of threads (thread count)
The current number of threads.
Commit Total
The number of pages currently committed by the system. Note that page commit (using VirtualAlloc with MEM_COMMIT) changes this value immediately. However, physical memory will not be charged until the pages are accessed.
Commit Limit
The current maximum number of pages that can be committed by the system without expanding the paging file. This number may change when memory is added or deleted, or when swap files have been enlarged, reduced, or added. If the paging file can be expanded, this is a soft limit.
Commit Peak
The maximum number of pages that have been in committed state since the last time the system was rebooted.
3.) Questions and answers about RAM, physical memory, kernel, etc.!
1. What does "physical memory" mean and how does its size vary?
- Physical memory, also called RAM, refers to the actual memory of a computer that can directly process its data. Its size varies depending on the RAM modules installed and can be changed by adding or removing RAM modules.
2. How is physical memory defined and what information does the system cache give?
- Physical memory is all the installed RAM in the computer. The system cache gives information about how much physical memory is currently being used to allocate pages of open files.
3. What is the role of physical memory in the system cache?
- Physical memory in the system cache is used to keep frequently used files or data in RAM to speed up access to them and improve overall system performance.
4. Why is the system cache important for memory allocation?
- The system cache is important because it allows the operating system to keep frequently used data in physical memory, resulting in faster access and more efficient use of memory.
5. What are the main functions of kernel memory?
- Kernel memory is used by the operating system's kernel drivers and device drivers. Its main functions include managing memory resources for the running of the operating system and its drivers, and managing hardware accesses.
6. How are paged and nonpaged memory different in the kernel?
- Paged memory in the kernel can be copied to the page file to free up physical memory, while nonpaged memory remains in physical memory and is not copied to the page file.
7. What is the difference between kernel paged and kernel nonpaged?
- Kernel paged refers to the memory that is currently in the kernel paged pool, while kernel nonpaged refers to the memory that is currently in the kernel nonpaged pool.
8. How is block size in memory defined?
- Block size in memory is defined as the size of a block of memory in bytes, which is relevant for memory allocation and management.
9. Why is block size in memory relevant?
- The block size in memory is important because it determines how data is organized and managed in memory, which can impact the efficiency and performance of the system.
10. How is the number of handles in memory measured?
- The number of handles in memory is measured by counting how many open memory handles there are at any given time. These handles are used to manage resources such as files, processes or other objects.
11. Why is the number of handles in memory important for the system?
- The number of handles in memory is important because it can indicate how many resources such as files, processes or other objects are being managed in the system at the same time. A high number of handles can indicate a high workload and affect the overall performance of the system.
12. How many processes typically run in memory at the same time?
- The number of processes that typically run in memory at the same time depends on the type of system and its use. In an average operating system, dozens or even hundreds of processes can be active at the same time.
13. What is the role of the threads in memory?
- Threads are executable units within a process and play an important role in multitasking and parallel execution of tasks. They share the same address space and resources as the process they are running in, and thus affect memory usage.
14. What is Commit Total in Memory and How is it Calculated?
- Commit Total in Memory indicates the total number of pages currently committed by the system. It is calculated by counting all committed pages in the system.
15. Why is Commit Total an important metric for system performance?
- Commit Total is an important metric because it tells you how much virtual memory is being used by the system. A high Commit Total can indicate high memory usage and lead to performance issues.
16. How is Commit Limit in Memory determined?
- Commit Limit in Memory is set based on the current maximum number of pages that can be committed by the system without expanding the page file. This limit can change depending on the system configuration.
17. Why is Commit Limit an important indicator of memory usage?
- The commit limit is an important indicator because it shows the maximum amount of virtual memory that the system can use before performance problems can occur. Approaching or exceeding this limit can indicate high memory usage.
18. What is the commit peak in memory and what information does it provide?
- The Commit Peak in memory indicates the maximum number of pages that were in the committed state at the same time since the last system reboot. It provides information about the peak of memory usage in the system.
19. Why is Commit Peak an important parameter for memory management?
- The Commit Peak is an important parameter because it shows how close the system was to its maximum memory usage limit. This can help in planning and optimizing memory management to avoid bottlenecks.
20. How is Physical Memory Measured and What Role Does It Play?
- Physical Memory is measured by recording the amount of RAM actually installed in the computer. Its role is to temporarily store data and programs while they are running to enable fast access and improve the overall performance of the system.
21. What information does Physical Memory provide about the system?
- Physical Memory provides information about the total size of installed RAM in the system, the currently available amount of physical memory, and the memory utilization, which provides insight into the current memory resource usage.
22. How is Physical Available Memory defined and how is it calculated?
- Physical Available Memory refers to the amount of physical memory that is currently available for immediate reuse without first having to write the contents to the disk. It is calculated by summing the size of the standby, free, and zero lists in memory.
23. Why is Physical Available Memory important for system performance?
- Physical Available Memory is important because it represents the amount of RAM that is immediately available for running processes and applications without having to access the slower disk. Having sufficient available memory is critical for smooth system performance.
24. What is the System Cache and how does it affect system performance?
- The system cache is the memory used for temporarily storing data from files and programs to speed up access to frequently used information. It positively affects system performance by speeding up access to data and improving system efficiency.
25. What effect does the system cache have on memory usage?
- The system cache can affect memory usage by reserving memory for cached data. This can result in less physical memory being available for other purposes, but at the same time improves performance through faster accesses to cached data.
26. What is the maximum physical memory size and how is it determined?
- The maximum physical memory size is the total amount of RAM that a system can support. It is determined by the capabilities of the motherboard and operating system and can be expanded by adding or replacing RAM modules.
27. Why is the maximum physical memory size crucial for system capacity?
- The maximum physical memory size is crucial because it determines the overall capacity of the system to run multiple processes and applications simultaneously. A larger memory capacity allows the system to hold more data in RAM and improve performance.
28. How can I check my system's current memory resources?
- Your system's current memory resources can be checked using system monitoring tools such as Task Manager on Windows or Activity Monitor on macOS. These tools display information such as total memory size, utilization, and available memory amount.
FAQ 3: Updated on: 7 June 2024 13:40
