An initial formatting of a hard drive, which initializes the physical tracks on the surface or the internal data carriers!Contents:1.) ... The low-level format!
|
| (Image-1) Clean the free space and put the PC in standby mode! |
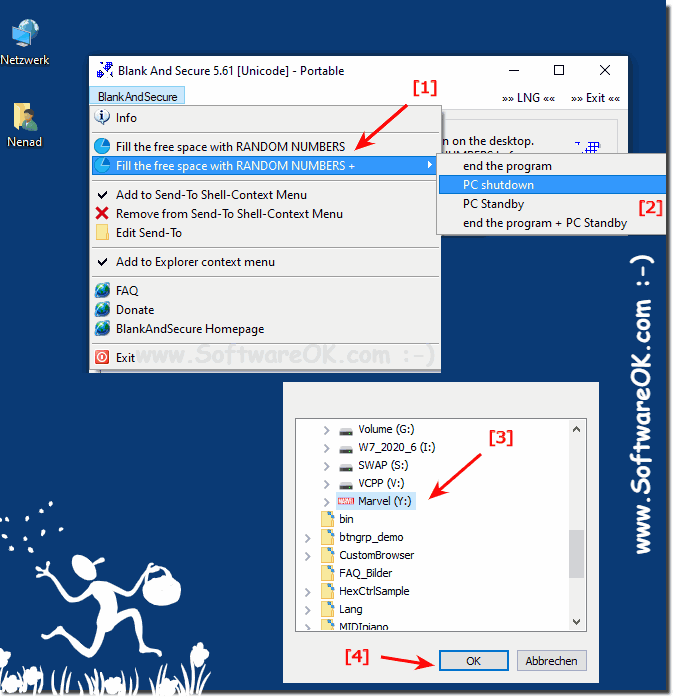 |
Info:
It is really very useful and advantageous to find these files that have not been safely deleted and then to delete them safely. It is a simple but effective tool for removing marks, it has been tested on everyone and has been successfully verified . As you can see above from the screenshot taken under Windows 10, it is easy to subsequently disguise deletion traces on the hard drive so that data protection is guaranteed, regardless of whether it is a Windows desktop, tablet, Surface Pro / Go, or even a Server operating system is.
It is really very useful and advantageous to find these files that have not been safely deleted and then to delete them safely. It is a simple but effective tool for removing marks, it has been tested on everyone and has been successfully verified . As you can see above from the screenshot taken under Windows 10, it is easy to subsequently disguise deletion traces on the hard drive so that data protection is guaranteed, regardless of whether it is a Windows desktop, tablet, Surface Pro / Go, or even a Server operating system is.
2.) A low-level format, explained technically correctly!
A low-level format, also known as physical formatting, is a process of preparing a storage medium, such as a hard drive or SSD, for use. Low-level formatting creates basic structures on the disk that allow the drive to store and read data. Here are the main features and steps of a low-level format:
1. Creating tracks and sectors:
The hard drive is divided into tracks and sectors. Tracks are concentric circles on the disk surface, while sectors are smaller sections within each track. This structure is necessary so that the read head knows the exact positions for writing and reading data.
2. Formatting the surface:
During the low-level format, the surface of the hard drive is checked and prepared for writing. Broken areas are identified and marked so that they are not used by the operating system.
3. Generating Error Correcting Codes (ECC):
To ensure data integrity, error correcting codes are generated and stored. These allow the drive to detect and correct errors in data storage and playback.
4. Creating control information:
Low-level formatting also writes control information and other necessary structures to the hard drive that help the drive work efficiently.
Historically, low-level formatting was a task performed by the user or technician, often using special utilities or BIOS features. However, these days low-level formatting is typically done at the factory during drive manufacturing, eliminating the need for end users to do it themselves.
It is important not to confuse low-level format with high-level format or file system format. High-level format refers to creating a file system (such as NTFS, FAT32, ext4) on the drive, which allows the operating system to organize and manage files and folders. The low-level format concerns the physical structuring of the disk itself, while the high-level format concerns the logical organization.
3.) Low-level format is a privilege of Windows, or does other OS also have it?
The low-level format is not an exclusive feature of Windows and is not specifically managed by operating systems such as Windows, macOS or Linux directly. Instead, low-level formatting is a fundamental process that is typically performed at the factory during the manufacturing of hard drives and SSDs. So it is a hardware related process that is independent of the operating system.Here are some important points for clarification:
1. Carried out by the manufacturer:
Nowadays, hard drive and SSD manufacturers perform the low-level format during the production process. This means that end users and administrators typically no longer feel the need to perform a low-level format.
2. Historical Relevance:
In the early days of hard drive technology, it was sometimes necessary for users or technicians to perform a low-level format themselves to prepare the disk for use. This was done using special utilities often provided by the manufacturer.
3. Operating system independent:
Low-level formatting is independent of the operating system. While Windows, macOS, Linux and other operating systems provide tools and commands for high-level formatting (creating file systems), they do not directly access low-level formatting. Operating systems interact with the hard drive at a higher level.
4. High-Level Format:
Most operating systems provide tools and commands for high-level formatting. For example, Windows offers the "Disk Management" tool and the `format` command, macOS has the `Disk Utility', and Linux offers commands such as `mkfs` to create file systems and format hard drives.
5. Hard Drive Utilities:
For deeper diagnostics and editing, many hard drive manufacturers offer special utilities that can run on different operating systems. These utilities can also provide functionality close to a low-level format, such as thorough disk erasing and testing, although a true low-level format is rarely necessary these days.
In summary, the low-level format is not a function of a specific operating system, but a hardware-related process that is typically carried out by the manufacturer. Operating systems focus on high-level formatting to create and manage file systems.
FAQ 196: Updated on: 21 May 2024 17:43
