But it is also important to check whether the Windows 11 virus protection is activated in order not to be surprised by ransomware or malware or other fours and Tojaners!Content: 1.) ... Security at a glance in Windows 11!
|
| (Image-1) Check whether the Windows 11 virus protection is activated! |
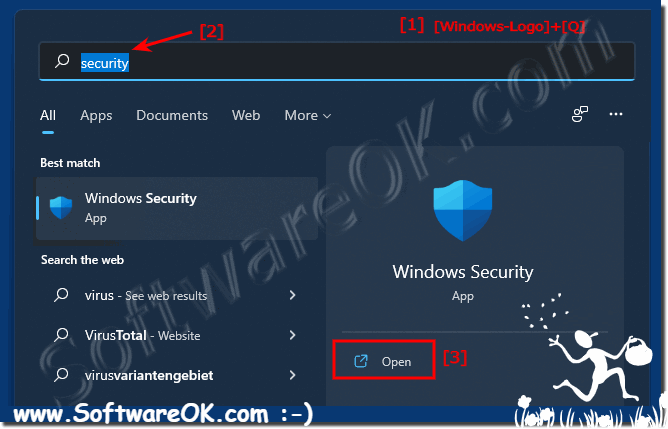 |
2.) Check whether all security settings are active!
Here is a simulated deactivation of Windows Defender. With a simple click on "Activate" all security options are activated and the green tick (everything OK) appears!
| (Image-2) Windows 11 virus protection is active! |
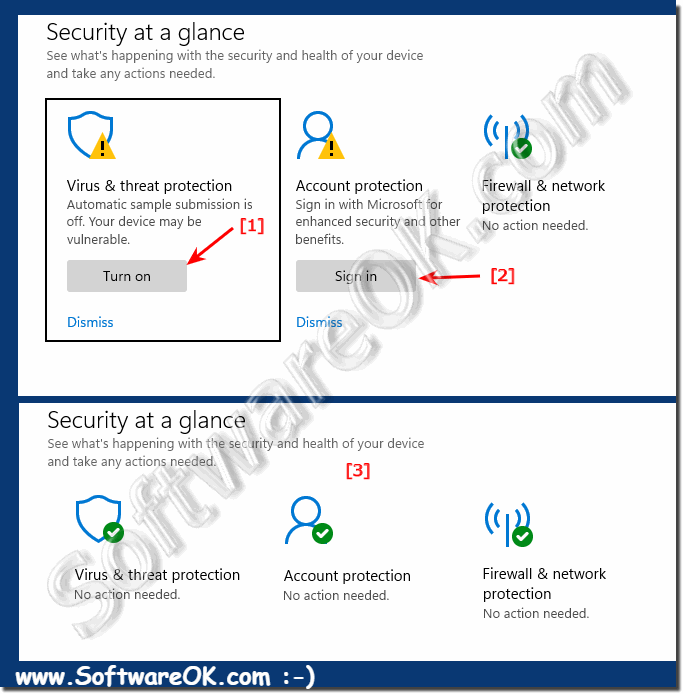 |
3.) How often should I check whether Windows 11 antivirus is active?
It is a good habit to regularly check if antivirus is active on your Windows 11 system. You can use the following guidelines as a guide:1. Weekly:
It is recommended to run a scan once a week to ensure that the antivirus is active and working properly.
2. After software updates:
After major software updates to Windows or antivirus software, run a check to ensure that settings have not changed and protection is still active.
3. After suspicious incidents:
If you notice any suspicious activity on your computer or suspect a possible infection, immediately check the antivirus status and conduct a thorough investigation.
4. If you make changes to security settings:
If you make changes to your computer's security settings, you should check your antivirus program to make sure it is still active and configured correctly.
5. Automatic monitoring:
It is also possible to set up automatic notifications or alerts to let you know when the antivirus is disabled or problems occur. This means you can react immediately if something is wrong.
Regular scans can help you ensure that your computer is adequately protected from malware and other threats. It's important to be proactive to minimize potential security risks.
4.) What are the most common reasons why a PC becomes infected with malware?
There are various ways a PC can become infected with malware. Here are some of the most common causes:
1. Phishing emails:
Opening fraudulent emails that claim to be from legitimate companies or people can result in malicious links being clicked or infected attachments being opened.
2. Unsafe websites:
Visiting unsafe websites that contain malicious code or serve as a platform for malware downloads can lead to infections, especially if you click on suspicious links or ads.
3. Downloads from Untrusted Sources:
Downloading software, files or media content from unsafe or untrustworthy sources on the Internet increases the risk of malware infection.
4. Software and operating system vulnerabilities:
Unpatched or outdated software, including the operating system and other applications, may contain security vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers to introduce malware.
5. USB devices and external media:
Connecting infected USB devices or opening files from external media, such as USB sticks or external hard drives, can result in malware being transferred to the computer.
6. Weak passwords and poor account security:
Using weak passwords or lack of two-factor authentication (2FA) can make it easier for attackers to access your system and carry out malicious activities.
7. Social Engineering:
Manipulative techniques such as social engineering can be used to trick users into revealing sensitive information or performing malicious actions that result in infection.
8. Peer-to-peer networks and illegal downloads:
Sharing files over peer-to-peer networks or downloading copyrighted content from illegal sources increases the risk of malware infection.
To minimize the risk of malware infection, it is important to take precautions such as: Examples include avoiding suspicious links and attachments, keeping software and operating systems updated, using antivirus software and firewalls, and raising awareness of security practices when handling digital content.
FAQ 77: Updated on: 15 April 2024 12:19
